TM 1-1510-218-10
3C-48
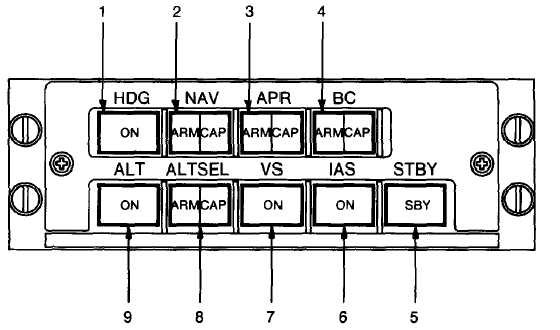
1. Heading Mode Selector
2. Navigation Mode Selector
3. Approach Mode Selector
4. Back Course Mode Selector
5. Standby Mode Selector
6. Indicated Airspeed Mode Selector
7. Vertical Speed Mode Selector
8. Altitude Preselect Mode Selector
9. Altitude Hold Mode Selector
Figure 3C-20. Flight Director Mode Selector
(b) VOR Approach Mode. The VOR
approach mode is selected by pressing the NAV
button on the mode selector with the navigation
receiver tuned to a VOR frequency and less than 20
DME miles from the station. The mode operates
identically to the VOR mode with the gains optimized
for a VOR approach.
(c) Localizer Mode. The localizer mode
is selected by selecting radio position with the NAV
Source Selector on the EFIS control panel and VOR 1
or VOR 2 as selected by the CRS 1/2 switch tuned to
a
localizer
frequency.
Mode
selection
and
annunciation in the LOC mode is similar to the VOR
mode. The localizer deviation signal is gain
programmed as a function of radio altitude, time, and
airspeed. If the radio altimeter is invalid, gain
programming is a function of glideslope capture, time,
and airspeed. If the radio altimeter is invalid, gain
programming is a function of glideslope capture, time,
and airspeed. Other valid logic is the same as the
VOR mode.
(3) Localizer Approach Mode (APR). The
approach mode is used to make an ILS approach.
Pressing the APR button with an ILS frequency tuned
arms both the NAV and APR modes to capture the
localizer and glideslope respectively. No alternate
NAV source can be selected. Operating LOC mode is
the same as described above except, if the radio
altimeter is invalid in APR mode, gain programming is
a function of glideslope capture, time, and airspeed.
With the APR mode armed, the pitch axis can be
in any one of the other pitch modes except go-around.
When reaching the vertical beam sensor trip point, the
system automatically switches to the glideslope mode.
The pitch mode and
APR
ARM
annunciators
extinguish and APR CAP annunciator illuminates on
the controller. At capture, a command is generated to
asymptotically
approach
the
glideslope
beam.
Capture can be made from above or below the beam.
The glideslope gain is programmed as a function of
radio altitude, time, and airspeed. The APR CAP
annunciator on the mode selector will extinguish if the
GS receiver becomes invalid after capture.
Glideslope capture is interlocked so that the
localizer must be captured prior to glideslope capture.
If the glideslope signal is not valid prior to capture, the
vertical beam sensor will not trip and the system will
remain in the pitch mode. After capture, if the NAV
receiver, GS receiver, compass data, or vertical gyro
becomes invalid, ADI command bars will bias out of
view. If the radio altimeter is not valid, the glideslope
gain programming will be a function of GS capture,
time, and airspeed.