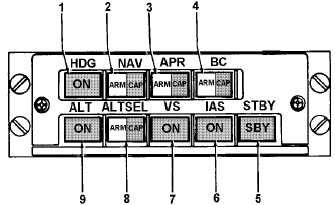
TM 1-1510-218-10
3B-27
1. Heading Mode Selector
6. Indicated Airspeed Mode Selector
2. Navigation Mode Selector
7. Vertical Speed Mode Selector
3. Approach Mode Selector
8. Altitude Preselect Mode Selector
4. Backcourse Mode Selector
9. Altitude Hold Mode Selector
5. Standby Mode Selector
Figure 3B-16. Flight Director/Mode Selector
(a) VOR Mode. The VOR mode is
selected by pressing the NAV button on the mode
selector with the navigation receiver tuned to a VOR
frequency and DME greater than 20 miles from the
station. Prior to VOR capture, the command cue
receives a heading select command as described
above and the HDG mode switch is illuminated along
with the NAV ARM annunciators. Upon VOR capture,
the system automatically: switches to the VOR mode;
HDG and NAV ARM annunciators extinguish; NAV
capture (NAV CAP) annunciators will illuminate. At
capture, a command is generated to capture and track
the VOR beam. VOR deviation is gain programmed
as a function of distance from the station. This
programming corrects for beam convergence thus
optimizing the gain through the useful VOR range. To
utilize this feature, the DME must be tuned to the
same VOR station as the NAV receiver that is feeding
the flight director. The course error signal is gain
programmed as a function of airspeed. Crosswind
washout is included, which maintains the aircraft on
beam center in the presence of crosswind. The
intercept angle and DME distance are used in
determining the capture point to ensure smooth and
comfortable performance during bracketing.
When passing over the station, an overstation
sensor detects station passage removing the VOR
deviation signal from the command until it is no longer
erratic. While over the station, course changes may
be made by selecting a new course on the HSI.
If the NAV receiver is not valid prior to the
capture point, the lateral beam sensor will not trip and
the system will remain in the HDG mode. After
capture, if the NAV receiver, compass data or vertical
gyro go invalid, the ADI command cue will bias out of
view. Also, the NAV CAP annunciators will extinguish
if the NAV receiver becomes invalid.
(b) VOR Approach Mode. The VOR
approach mode is selected by pressing the NAV
button on the mode selector with the navigation
receiver tuned to a VOR frequency and less than 20
DME miles from the station. The mode operates
identically to the VOR mode with the gains optimized
for a VOR approach.
(c) Localizer Mode. The localizer mode
is selected by pressing the NAV button on the mode
selector with the navigation receiver tuned to a LOC
frequency. Mode selection and annunciation in the
LOC mode is similar to the VOR mode. The localizer
deviation signal is gain programmed as a function of
radio altitude, time and airspeed. If the radio altimeter
is invalid, gain programming is a function of glide slope
capture, time and airspeed. Other valid logic is the
same as the VOR mode.
(3) Localizer Approach Mode (APR). The
approach mode is used to make an ILS approach.
Pressing the APR button with an ILS frequency tuned,
arms both the NAV and APR modes to capture the
localizer and glideslope respectively. No alternate
NAV source can be selected. Operating LOC mode is
the same as described above except, if the radio
altimeter is invalid in APR mode, gain programming is
a function of glideslope capture, time, and airspeed.