T.O. 1-1A-9
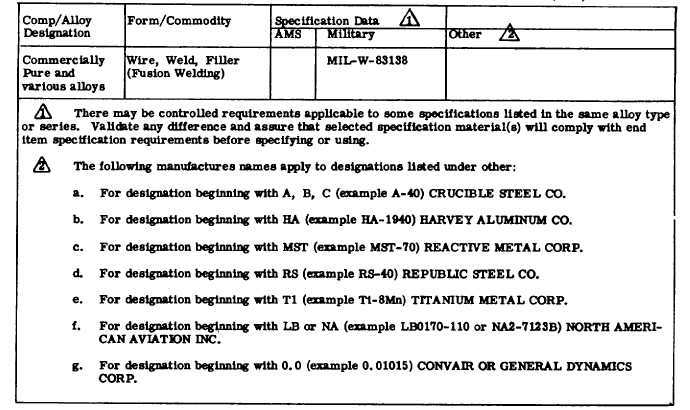
TABLE 5-1. SPECIFICATION CROSS REFERENCE TITANIUM ALLOYS (Cont).
5-16. FIRE DAMAGE. Fire damage to titanium and alloys becomes critical above 100°F due to the absorption of oxygen
and nitrogen from the air which causes surface hardening to a point of brittleness. However, an overtemperatured
condition is indicated by the formation of an oxide coating and can be easily detected by a light green to white color. If
titanium aircraft parts, the affected parts will be removed and replaced with serviceable parts.
5-17. HEAT TREATMENT-GENERAL
NOTE
MIL-H-81200, Heat Treatment of CAUTION Titanium and Titanium Alloys, will be the control
document for heat treatment of titanium and titanium alloys used on aerospace equipment.
For complete description of titanium heat treat requirements, refer to latest issue of MIL-H-
81200.
5-18. A majority of the titanium alloys can be effectively heat treated to strengthen, anneal and stress relieve. The
heating media for accomplishing the heat treatment can be air, inert atmosphere or vacuum shall be used as necessary
to protect all parts (titanium or titanium alloy), etc, which comprise the furnace load to prevent reaction with the elements
hydrogen, carbon, nitrogen and oxygen.
CAUTION
Cracked ammonia or hydrogen shall not be used as a protective atmosphere for titanium and
titanium alloys in any heat treating operation.
5-2C/(5-2D blank)