T.O. 1-1A-9
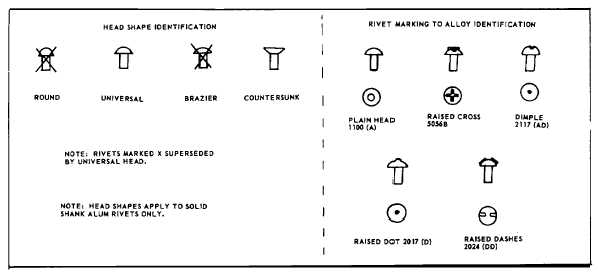
TABLE 3-17. GENERAL RIVET (ALUM) IDENTIFICATION CHART.
CAUTION
Heat treatment and most other operations
requiring use of heat will be accomplished
prior to installing rivets, since heating after
rivets are installed will cause warping and
possible corrosion if salt bath is used. The
salt from the bath will contaminate cracks
and crevices of the assembly and complete
removal cannot be assured.
3-168. Shear strength (ultimate) of a driven rivet can be
determined by the formula Ps=SsAN. Ps=ultimate
shear strength (pounds), Ss=specified shear strength of
the driven rivet (psi), A=cross sectional (area of the
driven rivet, normally equal to hole cross section
(square inch) and N=number of shear planes. For shear
strength of protruding and flush head rivets see Table 3-
19.
3-170. Rivet Selection. Unless otherwise specified,
rivets should be selected that have comparable strength
and alloy as material being assembled. This is an
important factor in preventing corrosion from dissimilar
metal
contact
and
to
assure
structurally
sound
assemblies. The following tables are provided as a
general guide for selection of rivet alloy vs. assembly
alloy.
3-171. The formula Ps = Sb AC can be used to
determine failure in bearing strength. Ps = ultimate
bearing strength of the joints (lbs), Sb = specified
ultimate bearing strength of the plate (psi) and Ac =
projected crushing area (bearing area) of rivet, or
diameter (sq in) see Table 3-20 for typical bearing
properties of aluminum alloy plates and shapes.
3-172. Rivet hole preparation is one of the key factors
in controlling (1) successful upsetting of rivet head (2)
material separation and buckling which weakens the
structural strength of the rivet joint (3) corrosion attack
of rivets and material after equipment is placed in
service/use. The rivet hole should be drilled,
punched/reamed to size that allows the minimum
clearance (approximately 0.003 for thin sheet and up to
about 0.020 for 0.750 - 1.000 inch thick material)
required to insert rivet without forcing. Theoretical rivets
holes should be completed i.e., drilled, reamed to size,
deburred, chips removed that may lodge or be trapped
in between surface of metal and treated (anodized, etc.)
before starting to rivet assembly. The above cannot
always be accomplished, especially where the assembly
is large and requires the application of a large amount of
rivets due to hole tolerance and variations in holding
clamping/pressures. To overcome these problems
requires that holes be pilot drilled and reamed to size at
time rivet is to be installed. This method has a twofold
purpose (1) allows easy insertion of rivets, (2) prevents
elongation of rivet holes and resulting weakening of rivet
joint.
3-173. Rivet holes drilled/reamed after assembly is
started should be treated by coating with zinc chromate
primer or other approved material. Two methods for
coating rivets and improving protection of hole surfaces
from corrosion are:
3-37